Ad-hoc Testing
Ad-hoc testing is a type of Agile testing that is performed without following a formal testing process or a predefined plan. It is an informal method of testing that is done on-the-fly by testers who are trying to break the system. The primary aim of ad-hoc testing is to find defects that may not have been discovered during the normal testing process.
Ad-hoc testing is often used to supplement formal testing methods and can be performed at any stage of the software development lifecycle. It is a flexible approach that allows testers to take an unstructured approach to testing and try different test scenarios. This type of testing can also be used to validate the results of formal testing methods, ensuring that the software is working as expected.
Ad-hoc testing is a valuable tool for software development teams because it can help to identify critical defects that may have been missed during formal testing. For example, it can be used to test the software’s ability to handle unexpected inputs or to test the functionality of features that were not included in the original test plan. Additionally, ad-hoc testing can be used to validate the results of formal testing methods, ensuring that the software is working as expected.
The process of ad-hoc testing typically begins with the tester brainstorming potential test scenarios. The tester then selects a scenario and tests the software in a way that is not specified in the formal test plan. This could involve testing a feature in a different order than it was intended to be used or trying to enter invalid data into a field to see how the system responds.
Ad-hoc testing is often performed by experienced testers who have a deep understanding of the software and its underlying systems. This allows them to quickly identify potential issues and to perform tests that may not have been considered during the formal testing process. Additionally, ad-hoc testing can be performed by developers, who can use their expertise to test the software in unique ways that are not included in the formal test plan.
Types of Ad-hoc Testing
There are several types of ad-hoc testing, including:
- Pairwise Testing: This type of ad-hoc testing focuses on testing combinations of input values. The goal is to test every possible combination of inputs to ensure that the software can handle all possible scenarios.
- Exploratory Testing: This type of ad-hoc testing is performed by testers who have a deep understanding of the software and its underlying systems. The goal is to explore the software and identify any potential defects by trying different test scenarios.
- Monkey Testing: This type of ad-hoc testing involves randomly inputting data into the software to see how it reacts. The goal is to identify any issues with the software’s handling of unexpected inputs.
- Error Guessing Testing: This type of ad-hoc testing involves testers using their experience and intuition to identify potential defects. The goal is to use their knowledge of the software to identify potential areas of weakness and to test these areas thoroughly.
- Briefcase Testing: This type of ad-hoc testing involves testers testing the software on different devices and platforms. The goal is to ensure that the software is compatible with all devices and platforms and that it works as expected in each environment.
- Day-to-Day Testing: This type of ad-hoc testing is performed by end-users and is focused on ensuring that the software works as expected in their daily work environment. The goal is to identify any issues with the software’s usability or functionality.
- Random Testing: This type of ad-hoc testing involves selecting test cases at random and testing them. The goal is to identify any potential defects in the software and to validate the results of other testing methods.
Each type of ad-hoc testing has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best approach depends on the specific needs of the project. However, all types of ad-hoc testing provide a flexible and informal approach to testing that can help to identify critical defects that may have been missed during formal testing.
Advantages and disadvantages of Ad-hoc Testing
One of the key benefits of ad-hoc testing is that it is a flexible approach that can be adapted to suit the needs of the project. This allows testers to respond to changing requirements and to test new features as they are developed. Ad-hoc testing can also be performed in parallel with other testing methods, which helps to speed up the overall testing process.
Another benefit of ad-hoc test is that it can be performed on a small scale, which means that it is less expensive and less time-consuming than other testing methods. This makes it an ideal testing method for projects with limited resources, such as small startups or projects with limited budgets.
However, ad-hoc test also has some disadvantages. One of the biggest disadvantages is that it is an informal approach to testing, which means that it is less structured and less controlled than other testing methods. This can lead to inconsistencies in the testing process and to a higher risk of human error. Additionally, ad-hoc test can be time-consuming, as testers must think of potential test scenarios and perform the tests.
Ad-hoc test is also less repeatable than other testing methods, which can make it more difficult to validate results and to compare results from one test to another. This can also make it more difficult to identify the root cause of a defect, as the testing process is not well documented.
Ad-hoc Test for Jira
AgileTest Test Management supports ad-hoc testing by providing flexible testing management capabilities within the Jira platform. Ad-hoc testing refers to an informal and unplanned approach to testing, where the tester can test any aspect of the application at any time. With AgileTest for Jira, testers can quickly create and manage ad-hoc tests, track their progress, and report results, all within the same platform as their other testing activities.
One of the key features of AgileTest for Jira is its ability to support ad-hoc testing through the use of test scripts and test sessions. Testers can create custom scripts or sessions on the fly and associate them with specific Jira issues, allowing them to easily track and manage their ad-hoc testing activities. Additionally, AgileTest for Jira provides a comprehensive reporting system, enabling testers to view and analyze test results, identify areas of improvement, and share their findings with the rest of the team.
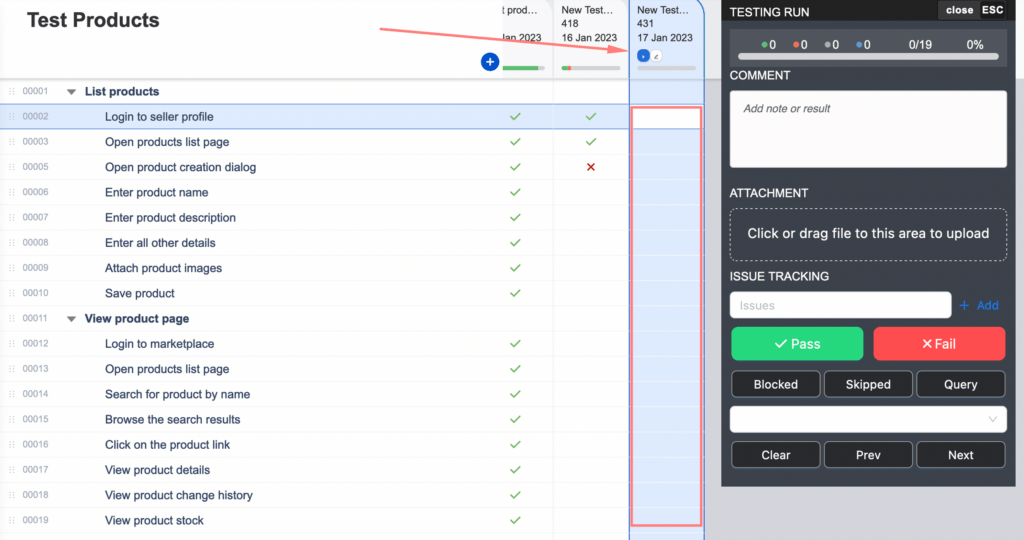
See more details here AgileTest Test Management for Jira